Exploring the Health Benefits of Kombucha 2024: Insights from Recent Research
Benefits of Kombucha Kombucha, a fermented tea known for its distinctive taste and potential health benefits, is becoming increasingly popular. Recent research,…
Benefits of Kombucha
Kombucha, a fermented tea known for its distinctive taste and potential health benefits, is becoming increasingly popular. Recent research, including a study published in PLOS Genetics, provides deeper insights into how kombucha might benefit health, particularly concerning lipid metabolism, gut health, and antioxidant properties.

The Study: Kombucha and Lipid Metabolism
Researchers utilized Caenorhabditis elegans, a type of nematode or roundworm, to study the effects of kombucha-associated microbes. This organism is commonly used in biological studies due to its simple anatomy and genetic similarities to humans. The study revealed that kombucha microbes could significantly reduce lipid accumulation by promoting lipophagy, a process where cells break down and recycle fats, resulting in smaller lipid droplets and reduced fat storage.
Microbial Interaction: The Key to Kombucha’s Benefits
A crucial aspect of kombucha’s health benefits is the complex interaction between bacteria and yeast, known as a symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast (SCOBY). This study emphasizes that these microbes work together in a symbiotic relationship, enhancing the overall health benefits of the beverage. The interaction between these microorganisms is vital for the fermentation process, which produces beneficial acids, probiotics, and other compounds that contribute to health.
Gut Health: Balancing the Microbiota
The study suggests that kombucha may help balance the gut microbiota, the community of microorganisms living in the digestive tract. A balanced microbiota is crucial for digestive health, immune function, and overall well-being. The probiotics in kombucha, introduced during fermentation, can aid in digestion, reduce inflammation, and support gut health by promoting a balanced microbial environment.
Antioxidant Properties: Combating Oxidative Stress
Another significant benefit highlighted by the study is kombucha’s antioxidant properties. The fermentation process enhances these properties, which can help combat oxidative stress—a condition caused by an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in the body. Oxidative stress is linked to aging and various chronic diseases. By neutralizing free radicals, antioxidants in kombucha can potentially reduce the risk of these conditions and promote overall health.
Brewing Kombucha: Essentials and Tips
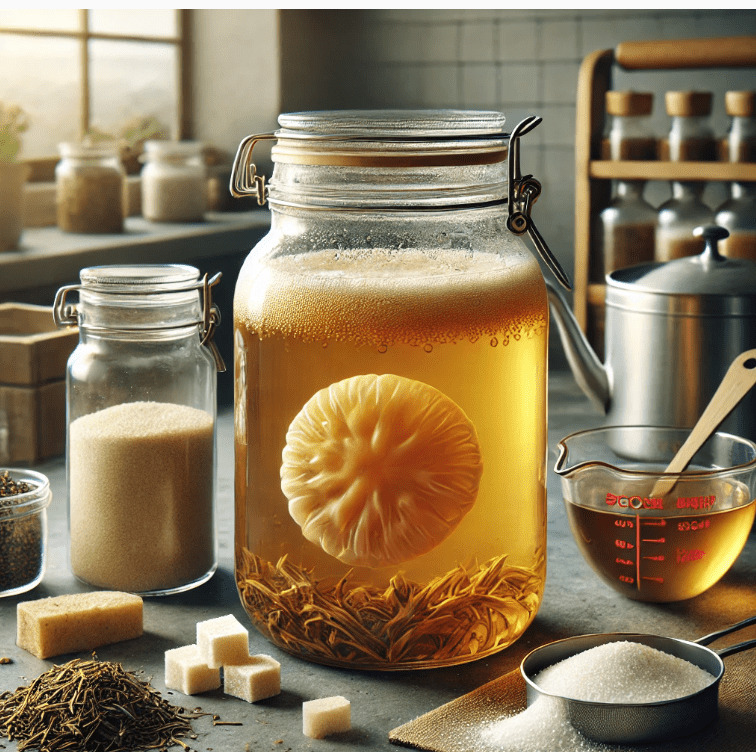
For those interested in making kombucha at home, here are some essential tips:
- Quality Ingredients: Use high-quality tea, filtered water, and sugar. These ingredients are crucial for developing the flavor and health benefits of kombucha.
- The SCOBY: Ensure your SCOBY is healthy and free from contaminants. It should be thick, opaque, and have a rubbery texture.
- Fermentation Process: Monitor the fermentation closely. The process typically takes 7 to 14 days, depending on temperature and taste preference.
- Flavoring: After the primary fermentation, add fruits, herbs, or spices to create unique flavors. This secondary fermentation can also enhance carbonation.

Health Considerations and Enjoyment
While kombucha has potential health benefits, it’s important to consume it in moderation. Those sensitive to caffeine or acidic foods should be cautious. Start with small amounts to see how your body reacts, especially if you’re new to kombucha.
Conclusion
The recent study adds to the growing body of evidence supporting the health benefits of kombucha. From aiding lipid metabolism and supporting gut health to providing antioxidant benefits, kombucha is more than just a trendy drink. Understanding these benefits can enhance your appreciation and enjoyment of kombucha.
The study titled “Kombucha Tea-associated microbes remodel host metabolic pathways to suppress lipid accumulation” was published on March 28, 2024, in PLOS Genetics. For more detailed scientific insights, you can read the full study here. Enjoy brewing and experimenting with flavors, and here’s to your health!






